Narayana-XA事务恢复
说事务恢复流程之前,我们来讨论下,会啥会出现事务恢复?XA二阶段提交协议不是强一致性的吗?要解答这个问题,我们就要来看看 XA 二阶段协议有什么问题?
问题一 :单点故障
由于协调者的重要性,一旦协调者 TM 发生故障。参与者RM会一直阻塞下去。尤其在第二阶段,协调者发生故障,那么所有的参与者还都处于锁定事务资源的状态中,而无法继续完成事务操作。(如果是协调者挂掉,可以重新选举一个协调者,但是无法解决因为协调者宕机导致的参与者处于阻塞状态的问题)
问题二 :数据不一致
数据不一致。在二阶段提交的阶段二中,当协调者向参与者发送 commit 请求之后,发生了局部网络异常或者在发送 commit 请求过程中协调者发生了故障,这回导致只有一部分参与者接受到了 commit 请求。而在这部分参与者接到 commit 请求之后就会执行 commit 操作。但是其他部分未接到 commit 请求的机器则无法执行事务提交。于是整个分布式系统便出现了数据不一致性的现象。
如何解决?
解决的方案简单,就是我们在事务的操作的每一步,我们都需要对事务状态的日志进行人为的记录,我们可以把日志记录存储在我们想存储的地方,可以是本地存储,也可以中心化的存储。Narayana 的开源版本,提供了file,db 2种方式存储,file 只能支持单机环境,而db是可以支持集群环境。
Narayana 事务恢复流程。
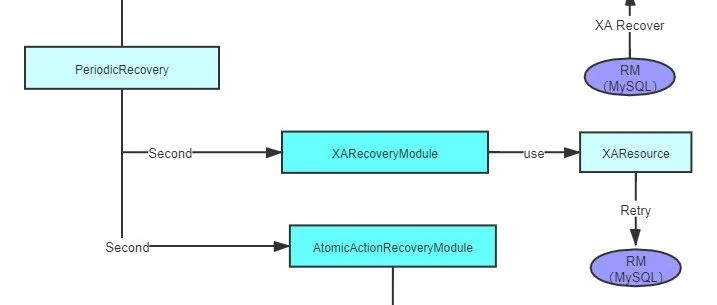
Narayana 使用了单线程轮询 RM,执行 XA recovery语句,来判断是否有需要恢复的语句。
具体的代码 com.arjuna.ats.internal.arjuna.recovery.PeriodicRecovery.run() 方法。以下是代码:
public void run ()
{
doInitialWait();
boolean finished = false;
do
{
boolean workToDo = false;
// ok, get to the point where we are ready to start a scan
synchronized(_stateLock) {
if (getStatus() == Status.SCANNING) {
// need to wait for some other scan to finish
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("PeriodicRecovery: background thread waiting on other scan");
}
doScanningWait();
// we don't wait around if a worker scan request has just come in
if (getMode() == Mode.ENABLED && !_workerScanRequested) {
// the last guy just finished scanning so we ought to wait a bit rather than just
// pile straight in to do some work
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("PeriodicRecovery: background thread backing off");
}
doPeriodicWait();
// if we got told to stop then do so
finished = (getMode() == Mode.TERMINATED);
}
} else {
// status == INACTIVE so we can go ahead and scan if scanning is enabled
switch (getMode()) {
case ENABLED:
// ok grab our chance to be the scanning thread
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("PeriodicRecovery: background thread Status <== SCANNING");
}
setStatus(Status.SCANNING);
// must kick any other waiting threads
_stateLock.notifyAll();
workToDo = true;
break;
case SUSPENDED:
// we need to wait while we are suspended
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("PeriodicRecovery: background thread wait while SUSPENDED");
}
doSuspendedWait();
// we come out of here with the lock and either ENABLED or TERMINATED
finished = (getMode() == Mode.TERMINATED);
break;
case TERMINATED:
finished = true;
break;
}
}
}
// its ok to start work if requested -- we cannot be stopped now by a mode change to SUSPEND
// or TERMINATE until we get through phase 1 and maybe phase 2 if we are lucky
if (workToDo) {
// ok it is now this thread's turn to run a scan. before starting we check if there is a
// worker waiting and reset the waiting flag. we will check again after the scan has
// completed to see if a worker request has come in after starting this scan.
// if so we avoid notifying the worker ensuring a requst is only confirmed when a
// full scan has happened afetr the request was made
boolean notifyRequired;
synchronized(_stateLock) {
notifyRequired = _workerScanRequested;
_workerScanRequested = false;
}
// we are in state SCANNING so actually do the scan
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("PeriodicRecovery: background thread scanning");
}
doWorkInternal();
// clear the SCANNING state now we have done
synchronized(_stateLock) {
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("PeriodicRecovery: background thread Status <== INACTIVE");
}
setStatus(Status.INACTIVE);
// must kick any other waiting threads
_stateLock.notifyAll();
// check if we need to notify a listener worker that we just finished a scan
if (notifyRequired && !_workerScanRequested) {
notifyWorker();
}
if (getMode() == Mode.ENABLED && !_workerScanRequested) {
// we managed a full scan and scanning is still enabled
// so wait a bit before the next attempt
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("PeriodicRecovery: background thread backing off");
}
doPeriodicWait();
}
finished = (getMode() == Mode.TERMINATED);
}
}
} while (!finished);
// make sure the worker thread is not wedged waiting for a scan to complete
synchronized(_stateLock) {
if (_workerScanRequested) {
notifyWorker();
}
}
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("PeriodicRecovery: background thread exiting");
}
}
- 别被吓到了,我们重点来关注
doWorkInternal();我们来看看这个方法。
//获取所有的RecoveryModule ,然后一个一个执行
Vector copyOfModules = getModules();
Enumeration modules = copyOfModules.elements();
while (modules.hasMoreElements())
{
RecoveryModule m = (RecoveryModule) modules.nextElement();
// we need to ensure we use the class loader context of the recovery module while we are executing
// its methods
ClassLoader cl = switchClassLoader(m);
try {
m.periodicWorkFirstPass();
} finally {
restoreClassLoader(cl);
}
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug(" ");
}
}
// take the lock again so we can do a backoff wait on it
synchronized (_stateLock) {
// we have to wait for a bit to avoid catching (too many)
// transactions etc. that are really progressing quite happily
doBackoffWait();
// we carry on scanning even if scanning is SUSPENDED because the suspending thread
// might be waiting on us to complete and we don't want to risk deadlocking it by waiting
// here for a resume.
// if we have been TERMINATED we bail out now
// n.b. if we give up here the caller is responsible for clearing the active scan
if (getMode() == Mode.TERMINATED) {
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("PeriodicRecovery: scan TERMINATED at phase 1");
}
return;
}
}
// move on to phase 2
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("Periodic recovery second pass at "+_theTimestamper.format(new Date()));
}
modules = copyOfModules.elements();
while (modules.hasMoreElements())
{
RecoveryModule m = (RecoveryModule) modules.nextElement();
ClassLoader cl = switchClassLoader(m);
try {
m.periodicWorkSecondPass();
} finally {
restoreClassLoader(cl);
}
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debugf("PeriodicRecovery: recovery module '%s' second pass processed", m);
}
}
- 首先会获取框架所有的
RecoveryModule类,然后一个一个执行,我们先来看看这个类:
public interface RecoveryModule
{
/**
* Called by the RecoveryManager at start up, and then
* PERIODIC_RECOVERY_PERIOD seconds after the completion, for all RecoveryModules,
* of the second pass
*/
public void periodicWorkFirstPass ();
/**
* Called by the RecoveryManager RECOVERY_BACKOFF_PERIOD seconds
* after the completion of the first pass
*/
public void periodicWorkSecondPass ();
}
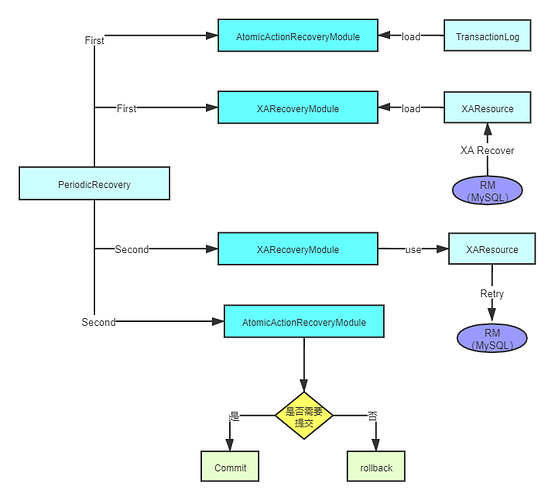
RecoveryModule 的实现类有 XARecoveryModule ,AtomicActionRecoveryModule,SubordinateAtomicActionRecoveryModule,CommitMarkableResourceRecordRecoveryModule。等4个实现类。
恢复执行第一个阶段
- XARecoveryModule :
它的作用就是执行XA recovery 命令从RM,获取 Xid数组。然后缓存起来。核心代码为:
//从数据库获取
trans = xares.recover(XAResource.TMSTARTRSCAN);
//缓存刷新
refreshXidScansForEquivalentXAResourceImpl(xares, trans);
- AtomicActionRecoveryModule:
从事务日志里面获取需要恢复的UID,具体代码为:
// Transaction type
boolean AtomicActions = false ;
// uids per transaction type
InputObjectState aa_uids = new InputObjectState() ;
try
{
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("AtomicActionRecoveryModule first pass");
}
AtomicActions = _recoveryStore.allObjUids( _transactionType, aa_uids );
}
catch ( ObjectStoreException ex ) {
tsLogger.i18NLogger.warn_recovery_AtomicActionRecoveryModule_1(ex);
}
if ( AtomicActions )
{
_transactionUidVector = processTransactions( aa_uids ) ;
}
恢复执行第二个阶段
首先执行的代码为 :
// move on to phase 2
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debug("Periodic recovery second pass at "+_theTimestamper.format(new Date()));
}
modules = copyOfModules.elements();
while (modules.hasMoreElements())
{
RecoveryModule m = (RecoveryModule) modules.nextElement();
ClassLoader cl = switchClassLoader(m);
try {
m.periodicWorkSecondPass();
} finally {
restoreClassLoader(cl);
}
if (tsLogger.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
tsLogger.logger.debugf("PeriodicRecovery: recovery module '%s' second pass processed", m);
}
}
- AtomicActionRecoveryModule: 进入
processTransactionsStatus(),最终会调用到com.arjuna.ats.arjuna.recovery.RecoverAtomicAction.replayPhase2()。我们来看看这个方法。
//省略无关代码
if ( (_theStatus == ActionStatus.PREPARED) ||
(_theStatus == ActionStatus.COMMITTING) ||
(_theStatus == ActionStatus.COMMITTED) ||
(_theStatus == ActionStatus.H_COMMIT) ||
(_theStatus == ActionStatus.H_MIXED) ||
(_theStatus == ActionStatus.H_HAZARD) )
{
super.phase2Commit( _reportHeuristics ) ;
}
else if ( (_theStatus == ActionStatus.ABORTED) ||
(_theStatus == ActionStatus.H_ROLLBACK) ||
(_theStatus == ActionStatus.ABORTING) ||
(_theStatus == ActionStatus.ABORT_ONLY) )
{
super.phase2Abort( _reportHeuristics ) ;
}
- 判断事务状态,如果是需要 commit 阶段的状态,进行 commit,否则进行 rollback
- XARecoveryModule : 尝试在进行恢复。核心代码为
private void bottomUpRecovery() {
for (XAResource xaResource : _resources) {
try {
xaRecoverySecondPass(xaResource);
} catch (Exception ex) {
jtaLogger.i18NLogger.warn_recovery_getxaresource(ex);
}
}
// JBTM-895 garbage collection is now done when we return XAResources {@see XARecoveryModule#getNewXAResource(XAResourceRecord)}
// JBTM-924 requires this here garbage collection, see JBTM-1155:
if (_xidScans != null) {
Set<XAResource> keys = new HashSet<XAResource>(_xidScans.keySet());
for(XAResource theKey : keys) {
RecoveryXids recoveryXids = _xidScans.get(theKey);
if(recoveryXids.isStale()) {
_xidScans.remove(theKey);
}
}
}
}
文章到此,已经写的很长很多了,我们分析了 ShardingSphere 对于 XA 方案,提供了一套 SPI 解决方案,对 Atomikos 进行了整合,也分析了 Atomikos 初始化流程,开始事务流程,获取连接流程,提交事务流程,回滚事务流程,事务恢复流程。
希望对大家理解 XA 的原理有所帮助。
关于我们
Apache ShardingSphere 是一套开源的分布式数据库中间件解决方案组成的生态圈,它由Sharding-JDBC、Sharding-Proxy 和 Sharding-Sidecar(规划中)这3款相互独立的产品组成。他们均提供标准化的数据分片、分布式事务、数据迁移、数据库治理和管控界面功能,可适用于如Java同构、异构语言、容器、云原生等各种多样化的应用场景。
Apache ShardingSphere 不断践行 Apache Way,致力于打造充满活力、规范、互助的社区!开源路上,我们欢迎你的加入。
项目地址:
更多信息请浏览官网:
https://shardingsphere.apache.org/
![]()
作者介绍:肖宇,Apache ShardingSphere Committer,开源hmily分布式事务框架作者, 开源soul网关作者,热爱开源,追求写优雅代码。目前就职于京东数科,参与ShardingSphere的开源建设,以及分布式数据库的研发工作。
感谢支持 OpenSEC